| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- top_k
- requests
- spark udf
- flask
- BigQuery
- session 유지
- Airflow
- correlation
- grad-cam
- GCP
- GenericGBQException
- Counterfactual Explanations
- airflow subdag
- TensorFlow
- Retry
- 공분산
- chatGPT
- login crawling
- UDF
- XAI
- subdag
- 유튜브 API
- tensorflow text
- hadoop
- integrated gradient
- youtube data
- 상관관계
- API
- API Gateway
- gather_nd
- Today
- Total
데이터과학 삼학년
GAN for Tabular Data (Data Augmentation) 본문
GAN for Tabular Data
| tabgan을 이용해 tabular data를 augmentation 해보자. gan은 이미지 데이터 생성에 매우 잘 알려져 있지만, tabular data에서는 잘알려져있지않다. tabgan의 원리를 이해하고, 샘플 코드를 통해 tabular 데이터를 증식(with GAN)하는 방법에 대해 알아보자. |
1. What is GAN
- GAN은 두개의 deep neural network로 구성됨(generator, discriminator)
- 두개의 모델은 동시에 학습됨. 일반적으로 모델의 구성도와 학습 절차는 아래 사진과 같음
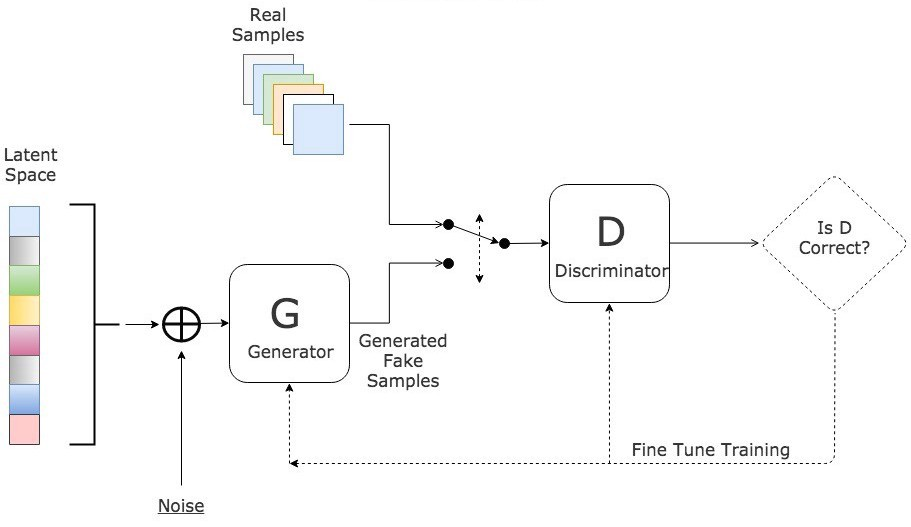
- generator의 역할은 real sample과 거의 유사한 sample을 만들어내는 것
- discrimator은 generator가 만들어낸 sample이 real sample인지 아닌지를 판단
- 위 두개의 모델이 생성과 판단을 반복하면서 결국 GAN은 real sample과 아주 유사한 형태의 sample을 만들어 낼 수 있게 됨
- 아래 그림은 실제로 StyleGAN2를 통해 만들어낸 이미지 데이터
- 데이터 자체를 만들어내는 것은 큰 문제는 아니지만, 모델의 무거움으로 인한 학습 속도와, 특정 도메인에서의 이미지 퀄리티는 개선될 필요가 있음
2. Tabular GANs
- 이미지 데이터를 생성하는데 있어 GANs이 많이 활용되고, 도메인도 중요하다는 사실들이 articles로도 많이 나오고 있음. 그럼 tabular에서 GAN은 어떨까?
Applying CTGAN to generating data for increasing train (semi-supervised)
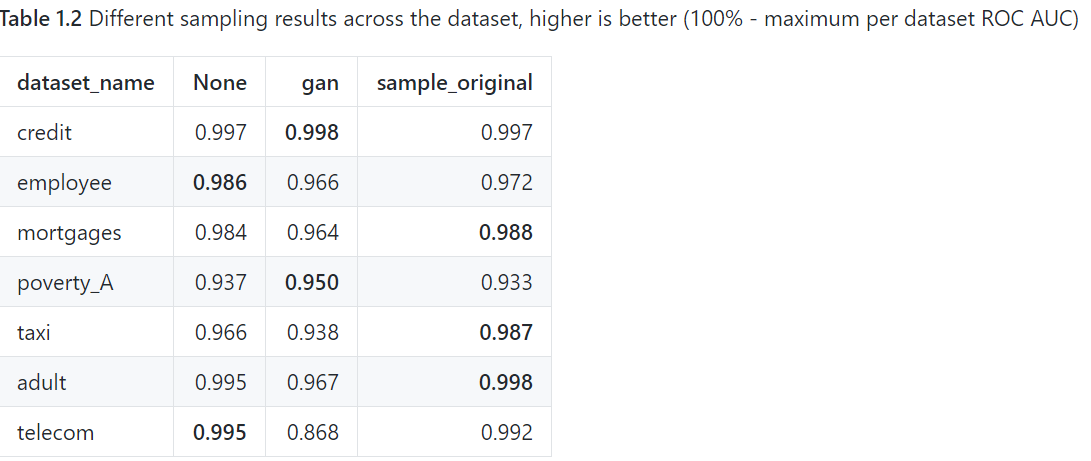
Experiment design
- T_train과 T_test로 데이터를 나누고, generator는 T_sync라는 데이터를 생성함
- T_train과 생성된 T_sync를 concatenated 하여 discriminator 모델, 즉 Adversarial training을 시킨다.
- 모델의 목적은 새롭게 학습된 adversarial model이 T_test라는 거의 유사한 데이터를 만들어내는 것이다.
- 여기서, 명심할것은 실제 truth라고 label된 데이터는 학습에 사용하지 않았다는 점이다.

- 위 모델을 이용한 결과
3. Code
from tabgan.sampler import OriginalGenerator, GANGenerator
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# random input data
train = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(10, 150, size=(50, 4)), columns=list("ABCD"))
target = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(50, 1)), columns=list("Y"))
test = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(100, 4)), columns=list("ABCD"))
# generate data
new_train1, new_target1 = OriginalGenerator().generate_data_pipe(train, target, test, )
new_train2, new_target2 = GANGenerator().generate_data_pipe(train, target, test, )
# example with all params defined
new_train3, new_target3 = GANGenerator(gen_x_times=1.1, cat_cols=None, bot_filter_quantile=0.001,
top_filter_quantile=0.999,
is_post_process=True,
adversaial_model_params={
"metrics": "AUC", "max_depth": 2,
"max_bin": 100, "n_estimators": 500,
"learning_rate": 0.02, "random_state": 42,
}, pregeneration_frac=2, only_generated_data=False,
epochs=500).generate_data_pipe(train, target,
test, deep_copy=True,
only_adversarial=False,
use_adversarial=True)import sklearn
def fit_predict(clf, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test):
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
return sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1])
dataset = sklearn.datasets.load_breast_cancer()
clf = sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=25, max_depth=6)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(
pd.DataFrame(dataset.data), pd.DataFrame(dataset.target, columns=["target"]), test_size=0.33, random_state=42)
print("initial metric", fit_predict(clf, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test))
new_train1, new_target1 = OriginalGenerator().generate_data_pipe(X_train, y_train, X_test, )
print("OriginalGenerator metric", fit_predict(clf, new_train1, new_target1, X_test, y_test))
new_train1, new_target1 = GANGenerator().generate_data_pipe(X_train, y_train, X_test, )
print("GANGenerator metric", fit_predict(clf, new_train1, new_target1, X_test, y_test))
#===
initial metric 0.9955593931170593
OriginalGenerator metric 0.9958060934994449
Fitting CTGAN transformers for each column: 100%
31/31 [00:09<00:00, 3.22it/s]
Training CTGAN, epochs:: 15%
74/500 [00:04<00:27, 15.51it/s]
GANGenerator metric 0.9929690391020106
참조
https://towardsdatascience.com/review-of-gans-for-tabular-data-a30a2199342
Review of GANs for tabular data
GANs are well-known for realistic image generation, but they can be also used in tabular data generation. Check it out in action
towardsdatascience.com
https://github.com/Diyago/GAN-for-tabular-data
GitHub - Diyago/GAN-for-tabular-data: We well know GANs for success in the realistic image generation. However, they can be appl
We well know GANs for success in the realistic image generation. However, they can be applied in tabular data generation. We will review and examine some recent papers about tabular GANs in action....
github.com
[참고]
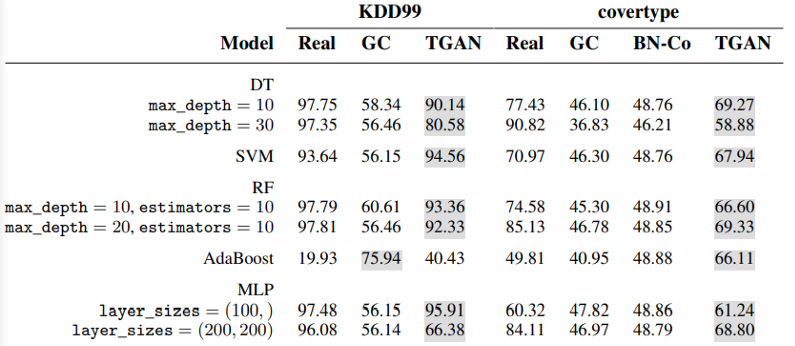
TGAN: Synthesizing Tabular Data using Generative Adversarial Networks
- TGAN 논문에 따르면 tabular 데이터를 만들어 내는데 GAN을 사용하는 것이 몇가지 문제가 있다고 말함
- the various data types (int, decimals, categories, time, text)
- different shapes of distribution ( multi-modal, long tail, Non-Gaussian…)
- sparse one-hot-encoded vectors and highly imbalanced categorical columns.
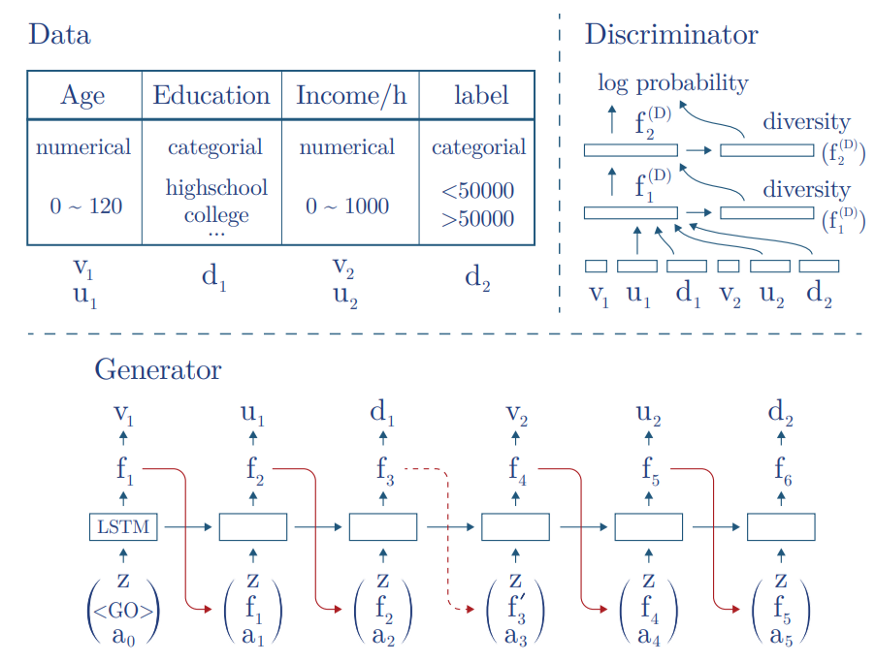
Task formalizing
- T라는 table이 n_c라는 연속형 변수와, n_d라는 이산형(categorical) 변수를 가지고 있는 테이블. 각 행을 C벡터
- 이 변수들은 잘 알지 못하는 P라는 분포를 가짐
- generator model은 M이고, M은 T_synth라는 sample data table을 만듦
- 머신러닝 모델은 real data table인 T_test를 가지고 데이터를 비교함
Preprocessing
- 연속형 변수 : Gaussian Mixture Model(GMM)을 이용하여 데이터 C를 V로 정규화 시킴
- 범주형 변수 : Due to usually low cardinality, they found the probability distribution can be generated directly using softmax. But it necessary to convert categorical variables to one-hot-encoding representation with noise to binary variables
After prepossessing, they convert T with n_c + n_d columns to V, U, D vectors. This vector is the output of the generator and the input for the discriminator in GAN. “GAN does not have access to GMM parameters”
Generator
'Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Tensorflow] tf.model prediction을 외부에서 child 프로세스로 만들어 멀티 프로세싱 적용이 어려운 이유 (0) | 2021.12.15 |
|---|---|
| 드롭아웃(dropout), 몬테 카를로 드롭아웃(Monte Carlo dropout) (0) | 2021.11.15 |
| AdaBoost (에이다부스트) (0) | 2021.08.11 |
| 스태킹 앙상블(stacked generalization in Ensemble) (1) | 2021.07.22 |
| Graph (python networkX) Metric 정리 (0) | 2021.07.20 |



